
Graphical interface
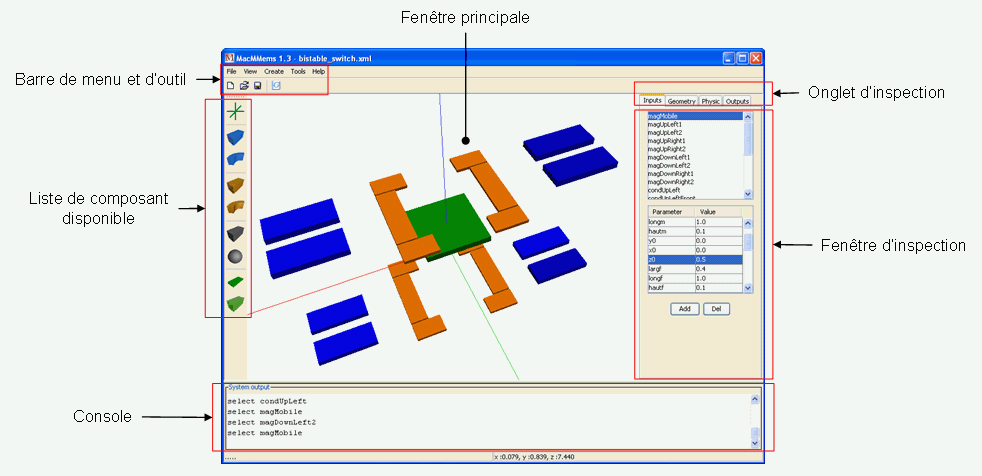
Modeling method
MacMMems is a modelling tool dedicated to the magnetic microsystem design. It is based on magnetostatic modelling with symbolic calculation of integrals :
Biot and Savart (for conductors):
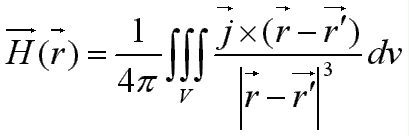
Coulombian equivalence (for magnets) :
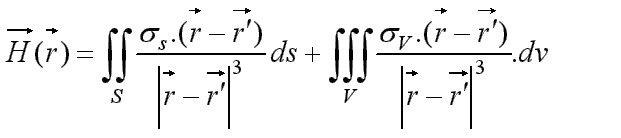 with
with 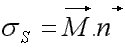 and
and 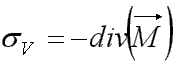
Forces and torques are then defined by integral expressions of the fields created by each sources.
Biot and Savart (for conductors):
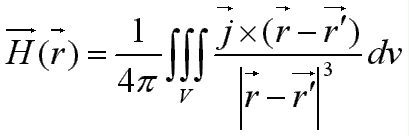
Coulombian equivalence (for magnets) :
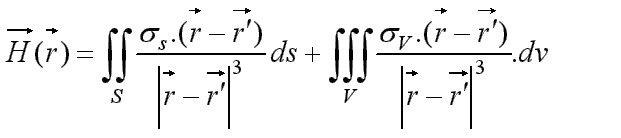 with
with 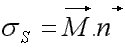 and
and 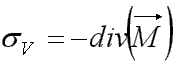
Forces and torques are then defined by integral expressions of the fields created by each sources.
Semi-analytical modelling
MacMMems is an equation generator, indeed, it produce a semi-analytical model which can be used by CADES framework for simulation or optimisation needs.
Application exemple : optimization of a magnetic µ-switch
Description
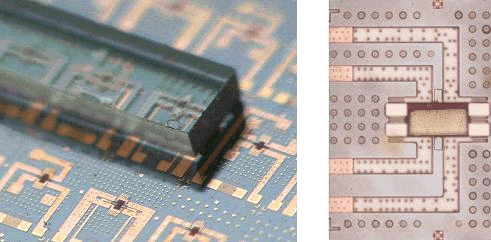
- 4 fixed magnets
- 1 mobile magnet
- 4 conductors
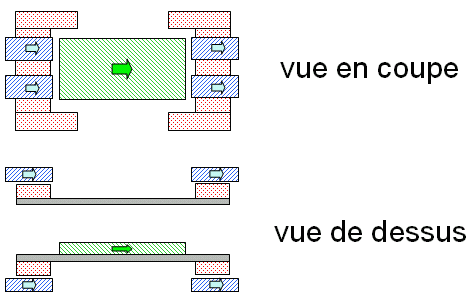
Design specifications
- 14 parameters to optimize
- 12 parameters to contrain
- To keep a force during displacement > 0.5 µN
- To ensure a choc resistance < 15 G
- To minimize copper losses
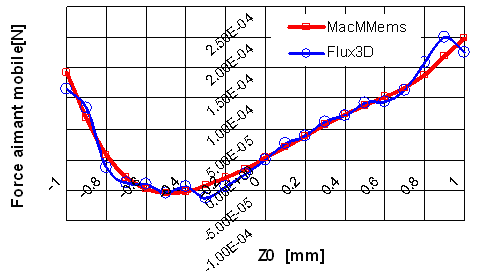
Finite elements comparison
In the case of simple geometries, analytical method are better than numerical ones due to numerical noise brought by meshing. Computation time is also better (1h30 vs 10 secondes for the analytical model)

Optimization
Sensitivity computation is automatically generated by CADES Framework leading to gradient based optimization algorithm use.
The optimized solution answer specifications, minimizing impulsionnal switching power to 31W.
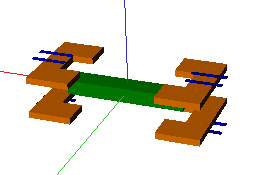
The optimized solution answer specifications, minimizing impulsionnal switching power to 31W.

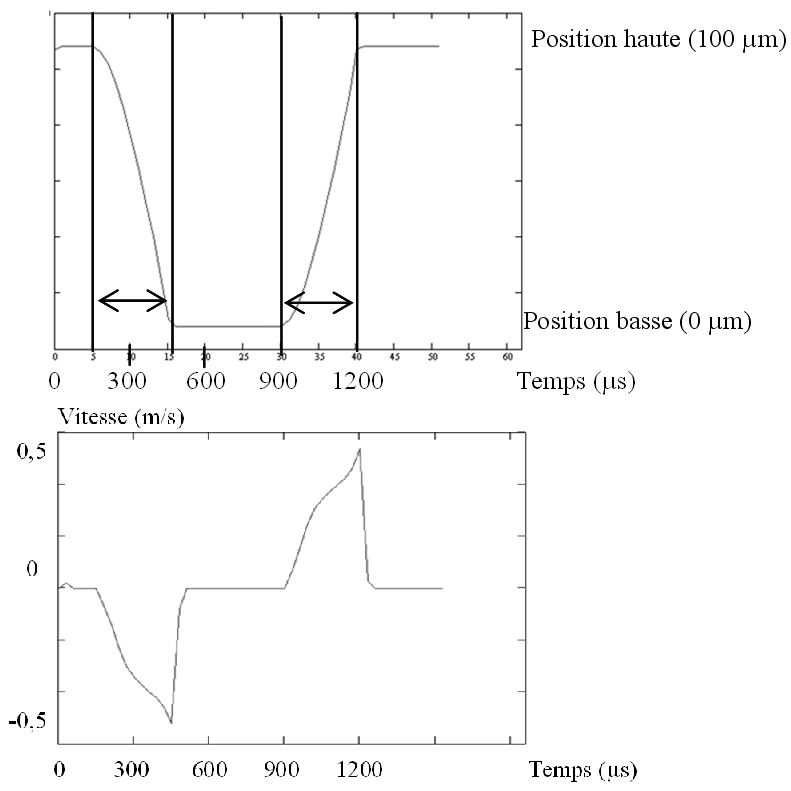
Dynamic study
The generated model is defined as a software component and can be easilly plugged into other environnements like Matlab/Simulink

References
- P. Pham-Quang, B. Delinchant, J.-L. Coulomb, “Reliability-based design optimization using local sensitivity with application to magnetic nano switch”, Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, IOSPress, ISSN 1383-5416, Volume 43, Number 1-2 / 2013
- H. L. Rakotoarison, V. Ardon, O. Chadebec, B. Delinchant, S. Guerin, J. L. Coulomb Formal Sensitivity Computation of Magnetic Moment method, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 44, Issue 6, June 2008 Page(s):1014 - 1017
- H. Chetouani, B. Delinchant, G. Reyne, Efficient modeling approach for optimization of a system based on passive diamagnetic levitation as a platform for bio-medical applications, COMPEL, Vol 26, Issue: 2, pp, 345 - 355, 2007
- H. L. Rakotoarison, J. P. Yonnet, B. Delinchant Using Coulombian approach for Modeling Scalar Potential and Magnetic Field of a Permanent Magnet with Radial Polarization, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics., Vol. 43, Issue 4, april 2007, pp 1261-1264, ISSN: 0018-9464
- H. Rostaing, J. Stepanek, B. Delinchant, J. Delamare, O. Cugat « Conception, modélisation et prototypage d'un micro-relais bistable magnétique » revue internationale de génie électrique (RIGE). 2005, vol 8 n_5-6, pp. 703-724

